Introduction to LLMs in Enterprise Apps
The question of where Large Language Models (LLMs) should be integrated into enterprise applications, and what roles they should play, is a crucial one. The answer is not a blanket "everywhere," but rather in specific areas where ambiguity arises in user input. This article explores how LLMs can enhance enterprise applications without requiring a complete overhaul, focusing on the intersection of traditional rule-based logic and LLM-assisted interpretations.
Understanding the Need for LLMs
In enterprise apps, user input can often be unstructured, leading to ambiguity that traditional rule-based systems struggle to address. This is where LLMs come into play, offering a way to interpret and make sense of ambiguous input. By identifying areas where ambiguity sneaks in, developers can determine where LLMs can be most effectively utilized.
Roles of LLMs in Enterprise Apps
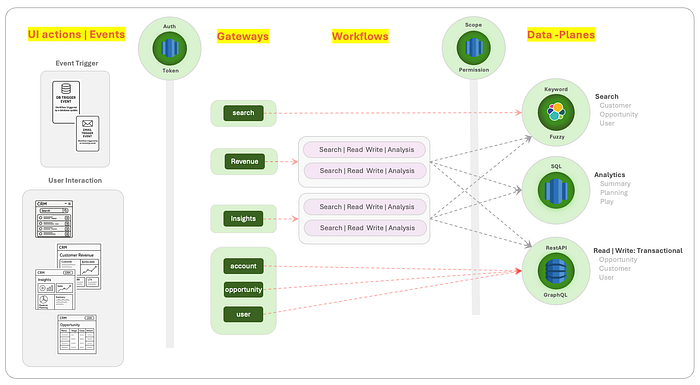
There are three critical roles that LLMs can play in enterprise environments:
- Action Agents: These LLMs focus on understanding the actions that users want to perform within the application. They help in interpreting the intent behind user input, ensuring that the system responds appropriately.
- Domain Agents: Domain Agents are responsible for understanding the context and domain-specific knowledge required to process user input. They ensure that the application’s response is not only accurate but also relevant to the user’s query or action.
- Workflow Routers: Workflow Routers use LLMs to determine the best workflow or process to follow based on user input. They help in routing the user’s request through the appropriate channels within the application, ensuring efficiency and reducing errors.
How LLMs Enhance Enterprise Apps
By integrating LLMs into these roles, enterprise applications can become more resilient and better equipped to handle ambiguous user input. The combination of traditional rule-based logic with LLM-assisted interpretations creates a system that can both follow strict rules when necessary and apply reasoning when faced with uncertainty. This duality is key to creating applications that are not only functional but also user-friendly and efficient.
Conclusion
In conclusion, LLMs have the potential to significantly enhance enterprise applications by addressing ambiguity in user input. By identifying the right areas for integration and leveraging LLMs in roles such as Action Agents, Domain Agents, and Workflow Routers, developers can create more robust, user-friendly, and efficient systems. This approach allows for the creation of applications that can handle a wide range of user inputs, from structured data to unstructured queries, making them more versatile and effective.
FAQs
- Q: What are LLMs, and how do they differ from traditional rule-based systems?
A: LLMs, or Large Language Models, are AI models designed to process and understand human language. They differ from traditional rule-based systems in their ability to interpret and reason about ambiguous or unstructured input. - Q: Where should LLMs be integrated into enterprise applications?
A: LLMs should be integrated into areas where ambiguity in user input is most likely to occur, such as in processing unstructured data or interpreting user intent. - Q: What are the benefits of using LLMs in enterprise apps?
A: The benefits include enhanced ability to handle ambiguous user input, improved user experience, increased efficiency, and the ability to create more resilient systems that combine the strengths of both rule-based logic and reasoning.