Introduction to Project Suncatcher
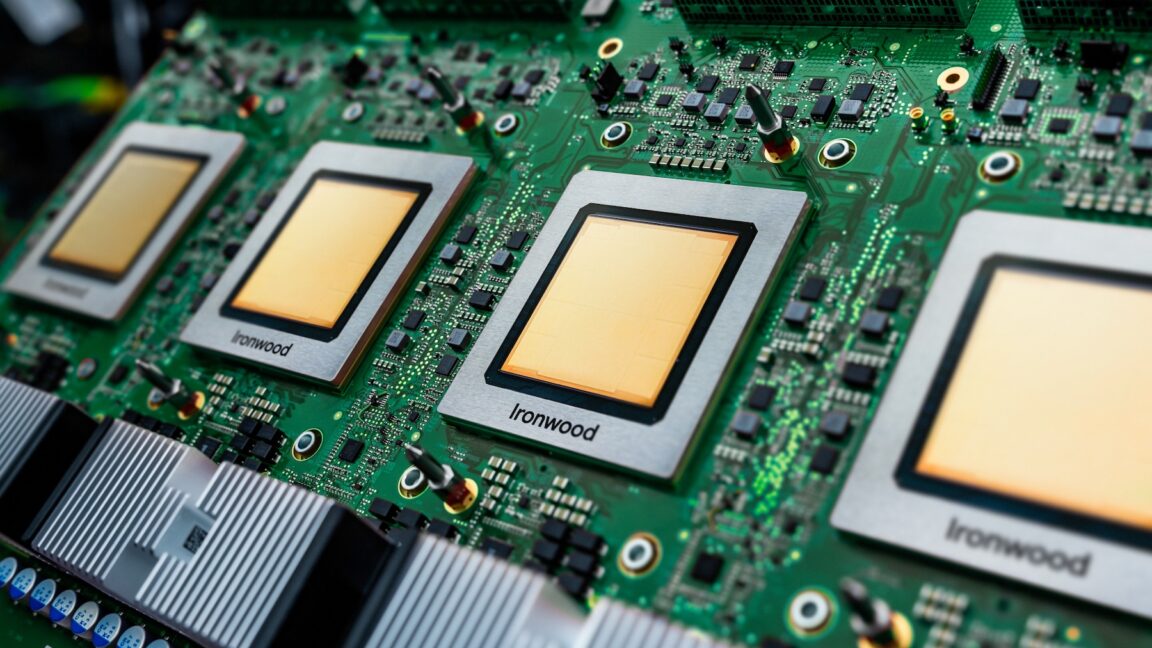
It was probably always a matter of when, not if, Google would add its name to the list of companies intrigued by the potential of orbiting data centers. Google announced a new initiative, named Project Suncatcher, to examine the feasibility of bringing artificial intelligence to space. The idea is to deploy swarms of satellites in low-Earth orbit, each carrying Google’s AI accelerator chips designed for training, content generation, synthetic speech and vision, and predictive modeling. Google calls these chips Tensor Processing Units, or TPUs.
The Concept Behind Project Suncatcher
“Project Suncatcher is a moonshot exploring a new frontier: equipping solar-powered satellite constellations with TPUs and free-space optical links to one day scale machine learning compute in space,” Google wrote in a blog post. The project aims to solve complex engineering challenges, including how to make TPUs withstand the intense radiation they will encounter in space. Google’s early tests show promise, but significant challenges still remain, such as thermal management and on-orbit system reliability.
The Why and How
Google published a research paper outlining the motivation for such a moonshot project. One of the authors, Travis Beals, spoke about Project Suncatcher and offered his thoughts on why it just might work. “We’re just seeing so much demand from people for AI,” said Beals, senior director of Paradigms of Intelligence, a research team within Google. “So, we wanted to figure out a solution for compute that could work no matter how large demand might grow.”
The Problem with Traditional Data Centers
Higher demand will lead to bigger data centers consuming colossal amounts of electricity. According to the MIT Technology Review, AI alone could consume as much electricity annually as 22 percent of all US households by 2028. Cooling is also a problem, often requiring access to vast water resources, raising important questions about environmental sustainability.
Conclusion
Project Suncatcher is an ambitious initiative that could potentially revolutionize the way we approach artificial intelligence and data processing. By deploying swarms of satellites in low-Earth orbit, Google aims to create a scalable and sustainable solution for machine learning compute. While there are still significant challenges to overcome, the potential benefits of Project Suncatcher make it an exciting and worthwhile pursuit.
FAQs
- What is Project Suncatcher? Project Suncatcher is a Google initiative that aims to deploy swarms of satellites in low-Earth orbit to scale machine learning compute in space.
- What are Tensor Processing Units (TPUs)? TPUs are Google’s AI accelerator chips designed for training, content generation, synthetic speech and vision, and predictive modeling.
- Why is Project Suncatcher necessary? Project Suncatcher is necessary to address the growing demand for AI and the environmental sustainability concerns associated with traditional data centers.
- What are the challenges facing Project Suncatcher? The challenges facing Project Suncatcher include thermal management, on-orbit system reliability, and withstanding intense radiation in space.