Introduction to CNC Machines
With the AI brain ready to make machining decisions, it was time to give it a body — the CNC machine itself. This phase focused on creating a fully functional three-axis dental CNC prototype, capable of interpreting AI-generated toolpaths and executing them precisely.
Building the CNC
The goal was clear:
Build a stable, compact, and intelligent CNC system that could cut, measure, and learn — all under local control.
CNC Hardware Overview
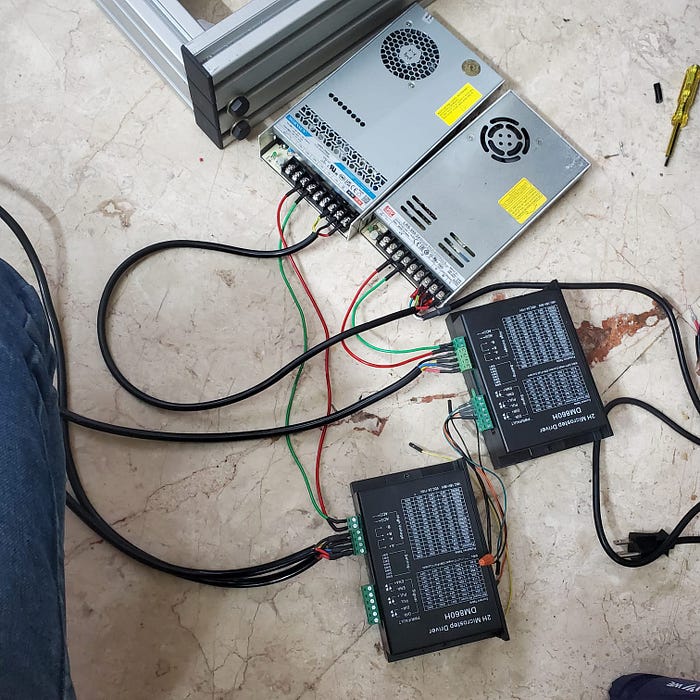
The CNC was built from the ground up as a prototype — from mechanical frame to firmware.
Mechanical Design
The mechanical design of the CNC machine includes:
- Axes: 3-axis gantry system (X, Y, Z) using linear rails and ball-screws.
- Work Envelope: 800 mm × 1800 mm × 300 mm — large enough for dental frameworks and precision prototypes.
- Spindle: ER20-collet, 24 000 RPM, 2.2 kW high-speed spindle, air-cooled, ideal for fine dental machining.
- Drive System: DM860H stepper drivers with NEMA 34 motors, micro-stepping configured for smooth motion.
- Frame: Rigid aluminum-extrusion structure for vibration stability and dimensional accuracy.
- Sensors: Limit switches on all axes, emergency stop, spindle-current sensor, and IMU vibration sensor for tool-health telemetry.
Electronics and Control
The electronics and control system of the CNC machine includes:
- Controller: Arduino-based GRBL v1.1 firmware on ATmega 328P.
- Power Electronics: 48 V supply for motors, 24 V for control logic and relays.
- Interface: USB serial (115 200 bps) connected to a host PC running the GRBL streamer.
- Telemetry Sensors:
- Spindle-RPM feedback (Hall sensor)
- Current feedback (Hall-effect transducer)
- 3-axis IMU vibration data
GRBL Firmware and Motion Control
At the heart of motion control lies GRBL v1.1, an open-source, lightweight G-code interpreter.
Why GRBL:
- Runs on inexpensive 8-bit hardware.
- Offers precise motion planning with acceleration control.
- Supports PWM-based spindle control and probing.
- Integrates easily with Python streaming libraries.
GRBL Streaming and Control Pipeline
For automated job execution, the AI-generated G-code must be transmitted line-by-line to GRBL.
We evaluated several open-source streamers:
Tool Selection for G-Code Streaming and Control
During development, we explored several tools to handle G-code streaming and CNC communication — each serving a different purpose in our workflow.
We began with bCNC and OpenCNCPilot.
OpenCNCPilot was especially useful in the early R&D stages. It offered visual feedback, height probing, and toolpath simulation — all of which helped us debug motion and surface consistency issues.
bCNC, on the other hand, proved valuable for interactive testing and calibration. Its macro system and probing support were essential when verifying tool offsets and machine accuracy.
Integration of AI and GRBL Control
The control pipeline links the AI Decision Engine with the CNC Execution System:
- AI Output: Machining meta (phase, tool, feed, step, plunge).
- CAM Generation: FreeCAD CLI builds toolpaths.
- Execution: G-code streamed via Python to GRBL.
- Monitoring: RPM, vibration, and current streamed through MQTT for feedback.
- Completion: Finished workpiece sent for 3-D scanning and inspection.
Summary
The 2.2 kW ER20 spindle-based CNC prototype brings the AI system’s decisions to life, turning predicted machining parameters into motion.
This physical embodiment closes the gap between data and material — allowing the machine to act, sense, and feed information back to improve subsequent cycles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CNC machine is a crucial component of the AI system, allowing it to execute its decisions and learn from its actions. The integration of the AI decision engine with the CNC execution system enables a closed-loop system that can improve its performance over time.
FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of the CNC machine in the AI system?
A: The CNC machine is the physical embodiment of the AI system, allowing it to execute its decisions and learn from its actions.
Q: What is GRBL and what is its role in the CNC machine?
A: GRBL is an open-source, lightweight G-code interpreter that controls the motion of the CNC machine.
Q: How does the AI system generate G-code for the CNC machine?
A: The AI system generates G-code through a CAM generation process using FreeCAD CLI.
Q: What is the role of the telemetry sensors in the CNC machine?
A: The telemetry sensors provide feedback to the AI system on the performance of the CNC machine, including RPM, vibration, and current.