Introduction to Scaling GenAI Applications
Designing a GenAI system that supports millions of users is challenging and requires continuous refinement and improvement. This article will discuss how to build a GenAI system that starts with single-user support and scales up to serve millions of users.
Understanding the Challenges of Scaling GenAI Applications
Scaling a GenAI application from zero to millions of users is a complex task. It involves designing a system that can handle a large volume of requests, process vast amounts of data, and provide fast and accurate responses. The system must be able to adapt to changing user demands, handle failures, and ensure high availability.
Key Components of a Scalable GenAI System
A scalable GenAI system consists of several key components, including:
- Databases: A database is used to store and manage data. Choosing the right database type is crucial for a scalable system.
- Web Servers: Web servers handle incoming requests and send responses to users. They must be able to handle a large volume of requests and provide fast responses.
- Scaling Strategies: There are two main scaling strategies: vertical scaling (increasing the power of a single server) and horizontal scaling (adding more servers).
Scaling Strategies for GenAI Applications
Vertical Scaling
Vertical scaling involves increasing the power of a single server by adding more resources such as CPU, memory, or storage. This approach is useful for small to medium-sized applications but has limitations, as a single server can only be scaled up to a certain point.
Horizontal Scaling
Horizontal scaling involves adding more servers to handle increased traffic. This approach is more flexible and can handle large volumes of traffic. However, it requires a load balancer to distribute traffic across multiple servers.
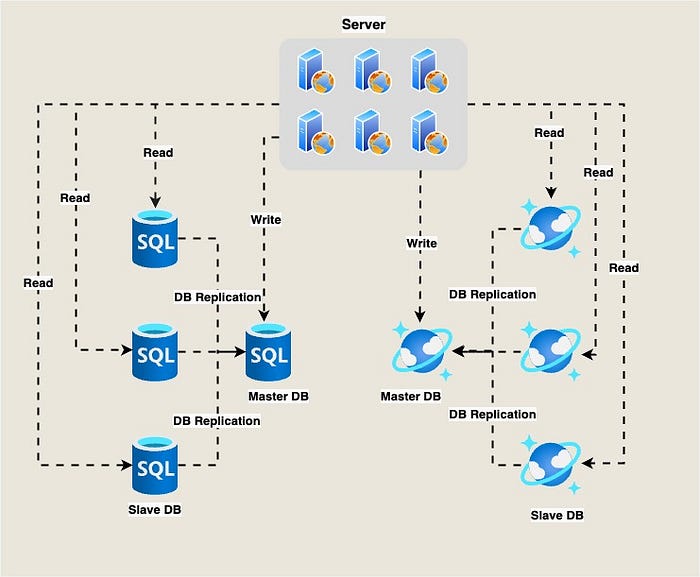
Database Replication and Caching
Database replication involves creating multiple copies of a database to improve availability and performance. Caching involves storing frequently accessed data in memory to reduce the time it takes to retrieve data. Both techniques are essential for improving the performance of a GenAI system.
Advanced Scaling Techniques
Load Balancing
Load balancing involves distributing traffic across multiple servers to ensure that no single server is overwhelmed. This technique is essential for horizontal scaling.
Semantic Caching
Semantic caching involves caching data based on its meaning rather than its location. This technique can improve performance by reducing the time it takes to retrieve data.
Token Limits
Token limits involve limiting the number of requests a user can make within a certain time period. This technique can help prevent abuse and ensure fair usage.
Conclusion
Scaling a GenAI application from zero to millions of users requires careful planning, design, and implementation. By understanding the challenges of scaling, choosing the right components, and using scaling strategies such as vertical and horizontal scaling, database replication, and caching, developers can build a scalable GenAI system. Advanced techniques such as load balancing, semantic caching, and token limits can further improve performance and ensure fair usage.
FAQs
- Q: What is the difference between vertical and horizontal scaling?
A: Vertical scaling involves increasing the power of a single server, while horizontal scaling involves adding more servers. - Q: Why is database replication important?
A: Database replication improves availability and performance by creating multiple copies of a database. - Q: What is caching, and how does it improve performance?
A: Caching involves storing frequently accessed data in memory to reduce the time it takes to retrieve data, improving performance. - Q: How can token limits help prevent abuse?
A: Token limits limit the number of requests a user can make within a certain time period, preventing abuse and ensuring fair usage.